A Privacy-Preserving Contact Tracing System based on a Publish-Subscribe Model
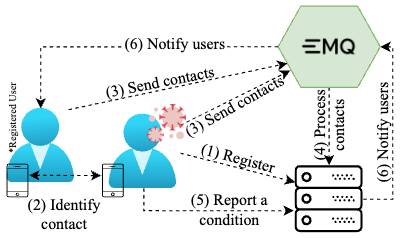
In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, using contact-tracking apps and measures such as social isolation and mask-wearing has emerged as an efficient strategy to mitigate the spread of the virus. Nonetheless, these apps have raised privacy concerns. This paper introduces a technique for enhancing Privacy in contact-tracing systems while preserving the data for research purposes. The contact-tracing system employs a unique identifier signed with a key associated with the application and the user. In this system, mobile devices serve as sensors sending beacons, actively detecting nearby devices, and transmitting the identifiers of surrounding contacts to a cloud-based platform. When a user reports a positive COVID-19 diagnosis, a dedicated web service identifies and tracks the identifiers associated with at-risk contacts. The system uses a topic-based publish-subscribe broker, and each identifier represents an individual topic to abstract contact communication and disseminate alert messages. To assess the system’s efficacy, we conducted a use case with twenty volunteers using the mobile application for two weeks, representing a small university campus. The quantitative results of the use case demonstrated the system’s capability of analyzing potential virus transmission and observing user’s social interactions while maintaining their anonymity.
Please cite:
@article{da2024privacy,
title={A Privacy-Preserving Contact Tracing System based on a Publish-Subscribe Model},
author={da Silva, Mikaella F and Santos, Bruno P and Rettore, Paulo HL and Mota, Vin{\'\i}cius FS},
journal={Journal of Internet Services and Applications},
volume={15},
number={1},
pages={244--257},
year={2024}
}
Mikaella F. da Silva, Bruno P. Santos, Paulo H. L. Rettore, Vinícius F. S. Mota.
Founding agencies: CNPq/CAPES/FAPEMIG.
Leave a comment